環境科学国際センター > English version of CESS homepage > Outline of reseach > Chemical substances and environmental radioactivity Group
ここから本文です。
ページ番号:69163
掲載日:2023年2月1日
Chemical substances and environmental radioactivity Group
The chemical substances and environmental radioactivity group conducts researches on environmental exposure of chemical substances (dioxins and persistent organic pollutants etc.) and environmental radioactivity that may affect human health and the ecosystem.
Under these circumstances, our studies include the following subjects to support countermeasures against environmental pollution caused by hazardous chemicals and radioactive materials.
- Monitoring of hazardous chemicals, radioactive materials, and its behaviors in the environment
- Development of analytical methods for micro-pollutants in various environmental media
- Environmental risk assessment for hazardous chemicals
Study on environmental pollution by hazardous chemicals
A study on contamination with halogenated flame retardants in Saitama Prefecture
Brominated flame retardant, hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) has been registered as Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in 2013, and its manufacture and usage are prohibited. Chlorinated flame retardant, Dechlorane Plus (DP) and related chemicals have drawn attention as environmental pollutants in recent years because of its POPs-like properties. We investigate the environmental levels and behaviors of brominated and chlorinated flame retardants in Saitama prefecture.
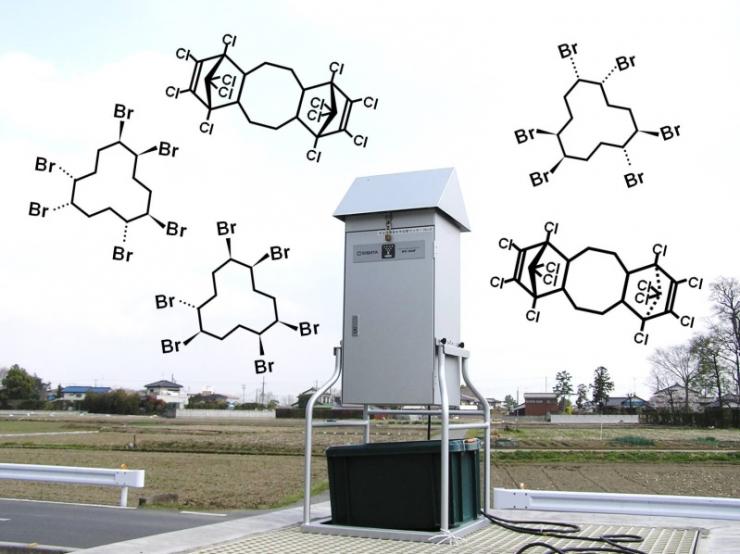
Sampling of flame retardants in the air
Studies on environmental methylsiloxanes: analytical and monitoring method development, distribution characteristics, and risk assessment
Cyclic methylsiloxanes have been widely used in personal care products, in the production of silicone polymer, and in a range of industrial applications. A part of cyclic methylsiloxanes (CMS) have been under heavy environmental scrutiny due to their persistence in the environment and bioaccumulative potency. However, the information concerning emission and distribution of CMS in the environment in Japan is still very limited. In view of an urgent need for environmental risk assessment of CMS, the objectives of present study include development of a high precision analysis of CMS in various environmental samples and occurrence of CMS in the environment from Saitama Prefecture.
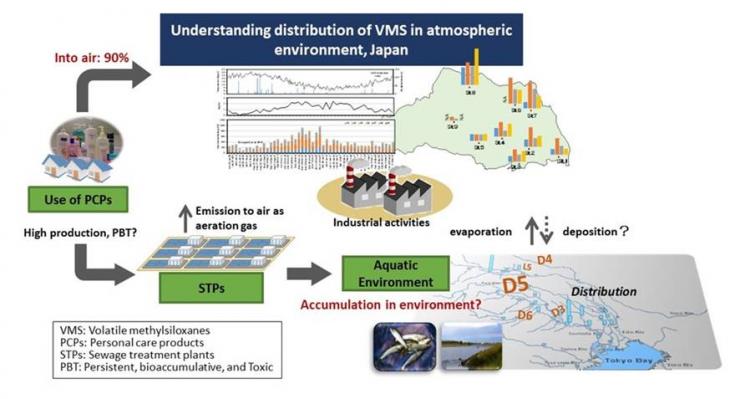
Environmental emission of methylsiloxanes
Environmental monitoring of dioxins in several polluted sites
The concentrations of dioxins in water and sediment in several sites of rivers in Saitama prefecture exceeds the environmental quality standard. We investigate the dioxin levels in these rivers to elucidate their sources and behaviors.
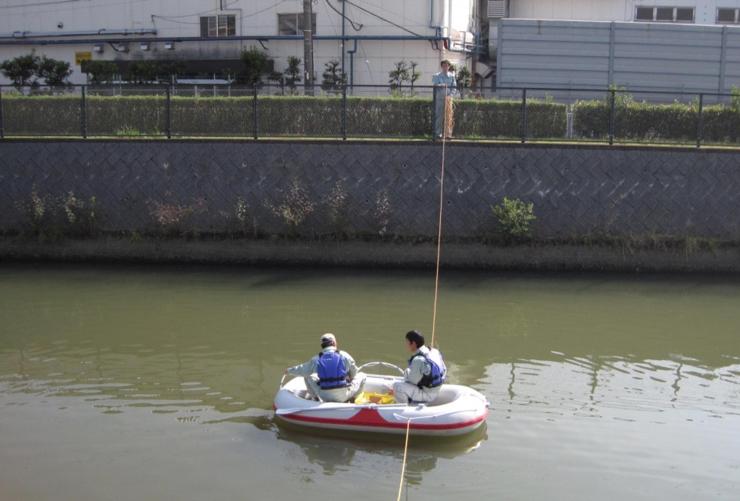

Collection of dioxins in river sediment
Development of methods for rapid analysis of hazardous chemical substances in the atmosphere and evaluation the risks posed by such substances in emergencies
The release of large amounts of hazardous chemical substances (HCSs) used in factories to the environment in accidents or disasters raises serious concerns about the effects of these substances on ecosystems and human health. However, standard analytical procedures and risk assessments for HCSs have not yet been fully established in Japan. For emergency readiness and quick response, in this study, we develop procedures for the rapid analysis of high-risk HCSs which are selected on the basis of their toxicity and amounts handled. Subsequently, HCS monitoring in the atmosphere around factories under non-emergency (in normal) conditions was conducted. Moreover, manual of assessing the risks posed by HCSs will be provided.
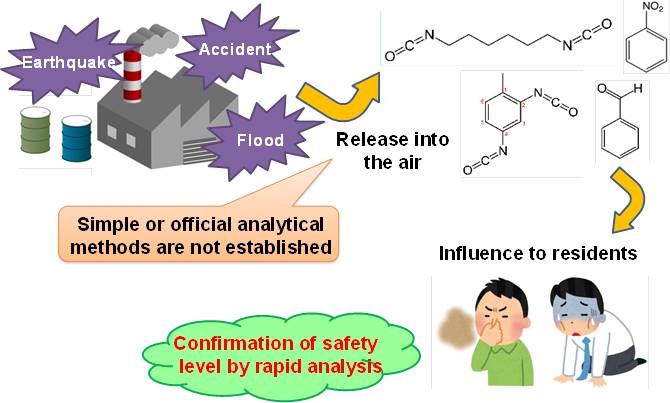
Background of the study
A study on the environmental behavior of radioactive materials in an ecological garden
Radioactive materials released into the atmosphere by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in March 2011 have since been transported by advection and diffusion to the Kanto Plain, where they have been deposited as fallout. Radioactive cesium, in particular has reached high concentrations in some areas of the plain. Cesium in fallout is distributed, transported, and accumulated in various environmental media. Therefore, the evaluation of transportation characteristics for cesium is need. To clarify environmental behavior of radioactive materials, in this study, we investigate concentrations of radioactive materials, especially radioactive cesium, in the soil, water, and biota collected from an ecological garden which has been constructed at our research center in Kazo City as a model of a relatively closed ecosystem environment.

Measurement of radiation dose by a germanium semiconductor detector
お問い合わせ